1Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Korea.
2College of Nursing · Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Korea.
Copyright © 2016 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article is a condensed form of the first author's master's thesis from Gyeongsang National University.
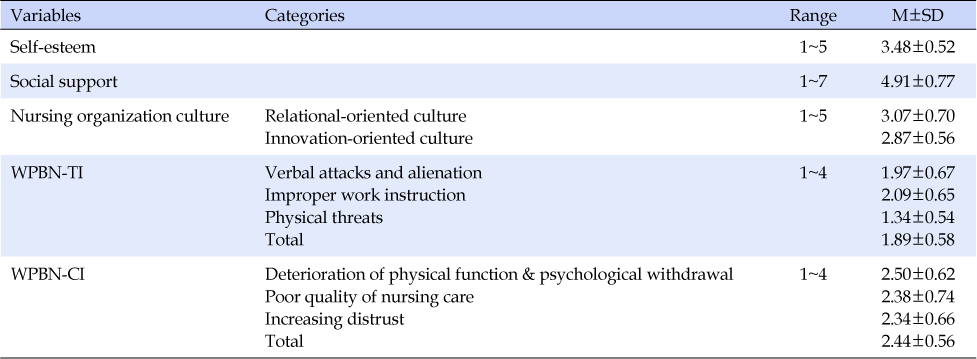

WPBN-TI=Workplace bullying in nursing type inventory; WPBN-CI=Workplace bullying in nursing consequence inventory.
WPBN-TI=Workplace bullying in nursing type inventory; WPBN-CI=Workplace bullying in nursing consequence inventory.
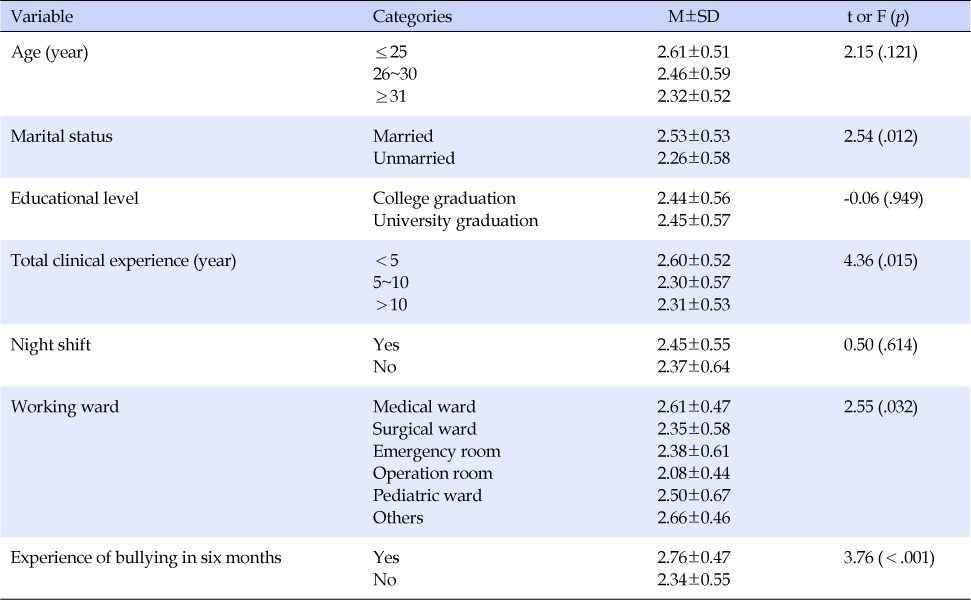
*p<.05, **p<.01; WPBN-TI=Workplace bullying in nursing type inventory.
WPBN-TI=Workplace bullying in nursing type inventory; WPBN-CI=Workplace bullying in nursing consequence inventory.
WPBN-TI=Workplace bullying in nursing type inventory; WPBN-CI=Workplace bullying in nursing consequence inventory.
*

