College of Nursing, Konyang University, Korea.
Copyright © 2016 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
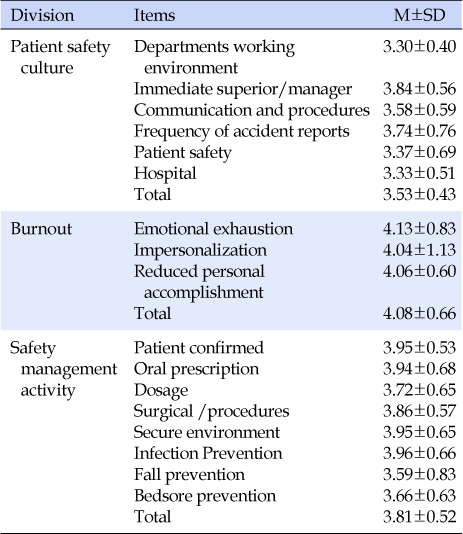
X1=Patient safety culture awareness; X2=Department work environment; X3=Immediate superior/manager; X4=Communication and procedures; X5=Frequency of accident reports; X6=Patient safety; X7=Hospital; X8=Perception; X9=Emotional exhaustion; X10=Impersonalzation; X11=Reduced personal accomplishment; X12=Safety management activity.
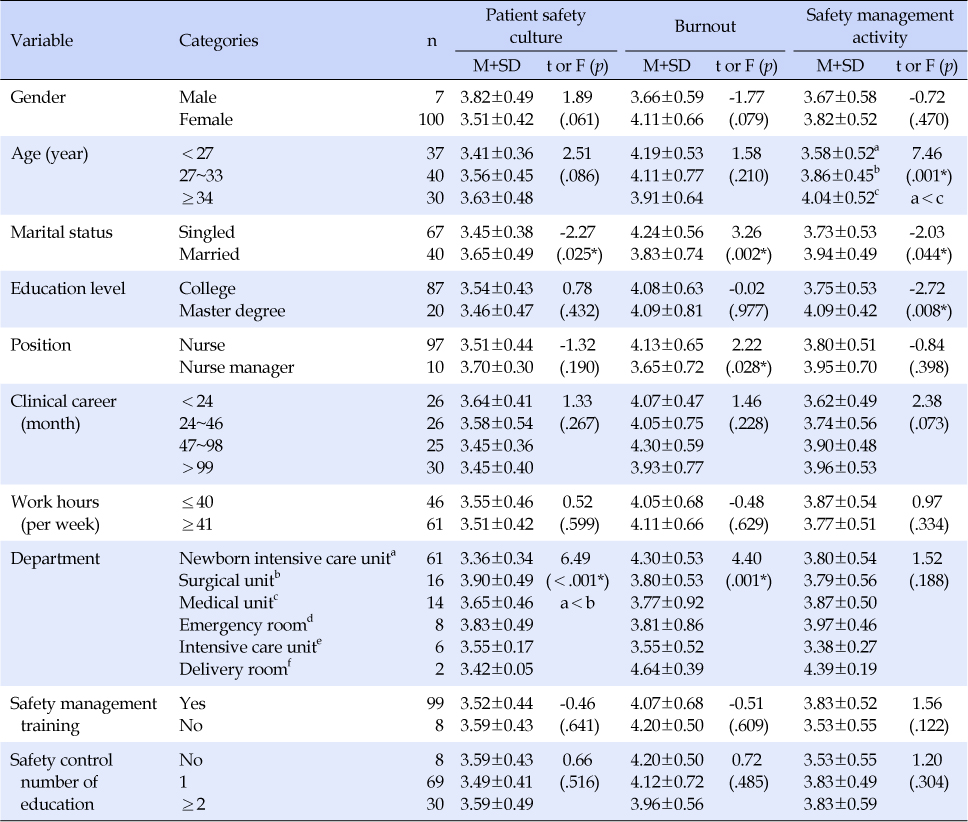
Variable: Patient safety culture=Score; Exhaustion=Score; Age (1=<27, 2=27~33, 3=≥34); Marital status (1=Singled, 2=Married); Education level (0=College, 1=Master degree); Position (0=nurse, 1=nurse manager); Department (1=Newborn intensive care unit, 2=Surgical unit, 3=Medical unit, 4=Delivery room, 5=Intensive care unit, 6=Emergency room).

*Sheffé test.
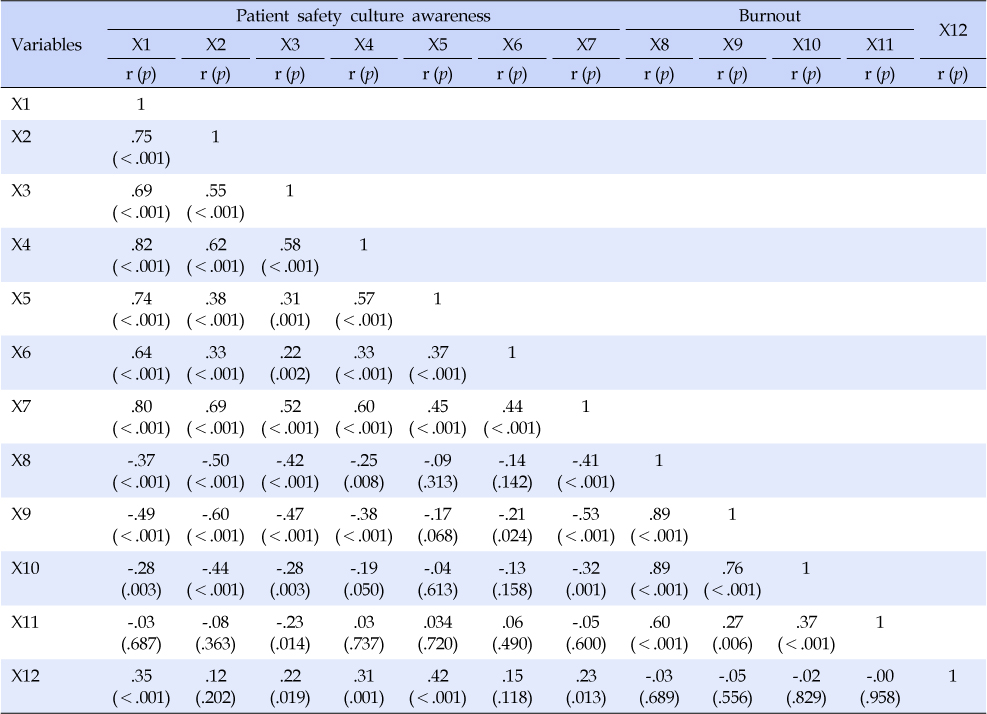
X1=Patient safety culture awareness; X2=Department work environment; X3=Immediate superior/manager; X4=Communication and procedures; X5=Frequency of accident reports; X6=Patient safety; X7=Hospital; X8=Perception; X9=Emotional exhaustion; X10=Impersonalzation; X11=Reduced personal accomplishment; X12=Safety management activity.
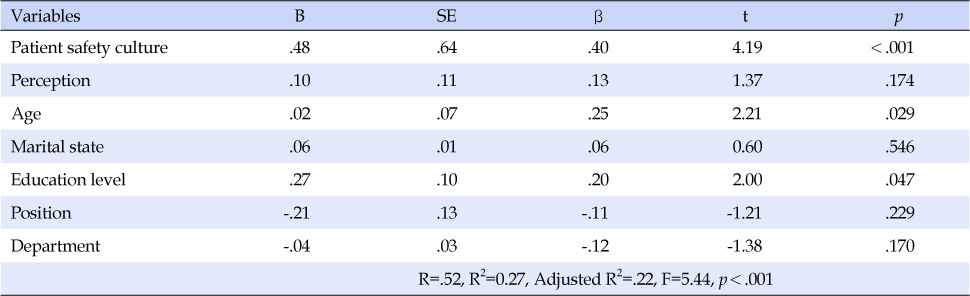
Variable: Patient safety culture=Score; Exhaustion=Score; Age (1=<27, 2=27~33, 3=≥34); Marital status (1=Singled, 2=Married); Education level (0=College, 1=Master degree); Position (0=nurse, 1=nurse manager); Department (1=Newborn intensive care unit, 2=Surgical unit, 3=Medical unit, 4=Delivery room, 5=Intensive care unit, 6=Emergency room).
*Sheffé test.
X1=Patient safety culture awareness; X2=Department work environment; X3=Immediate superior/manager; X4=Communication and procedures; X5=Frequency of accident reports; X6=Patient safety; X7=Hospital; X8=Perception; X9=Emotional exhaustion; X10=Impersonalzation; X11=Reduced personal accomplishment; X12=Safety management activity.
Variable: Patient safety culture=Score; Exhaustion=Score; Age (1=<27, 2=27~33, 3=≥34); Marital status (1=Singled, 2=Married); Education level (0=College, 1=Master degree); Position (0=nurse, 1=nurse manager); Department (1=Newborn intensive care unit, 2=Surgical unit, 3=Medical unit, 4=Delivery room, 5=Intensive care unit, 6=Emergency room).