1The Graduate School of Yonsei University, Korea.
2College of Nursing, Yonsei University, Korea.
Copyright © 2015 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

*Multiple responses; a, b, c, d=Scheffé test.
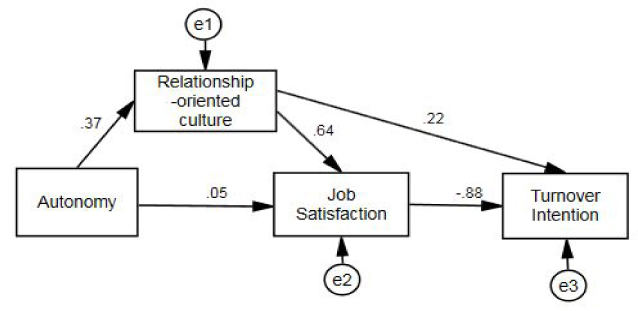
*Dummy variables: Position (Deputy manager=0), WH (55~60=0); JC=Job characteristics, OC=Organizational culture, WH=Work hours.
*SMC=Squared multiple correlation.
*Multiple responses; a, b, c, d=Scheffé test.
*Dummy variables: Position (Deputy manager=0), WH (55~60=0); JC=Job characteristics, OC=Organizational culture, WH=Work hours.
*SMC=Squared multiple correlation.