1College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Korea.
2College of Nursing · The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Korea.
Copyright © 2014 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This study was conducted with the assistance of the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service for their help with database.

General Characteristics of Hospitals (N=2,298)
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
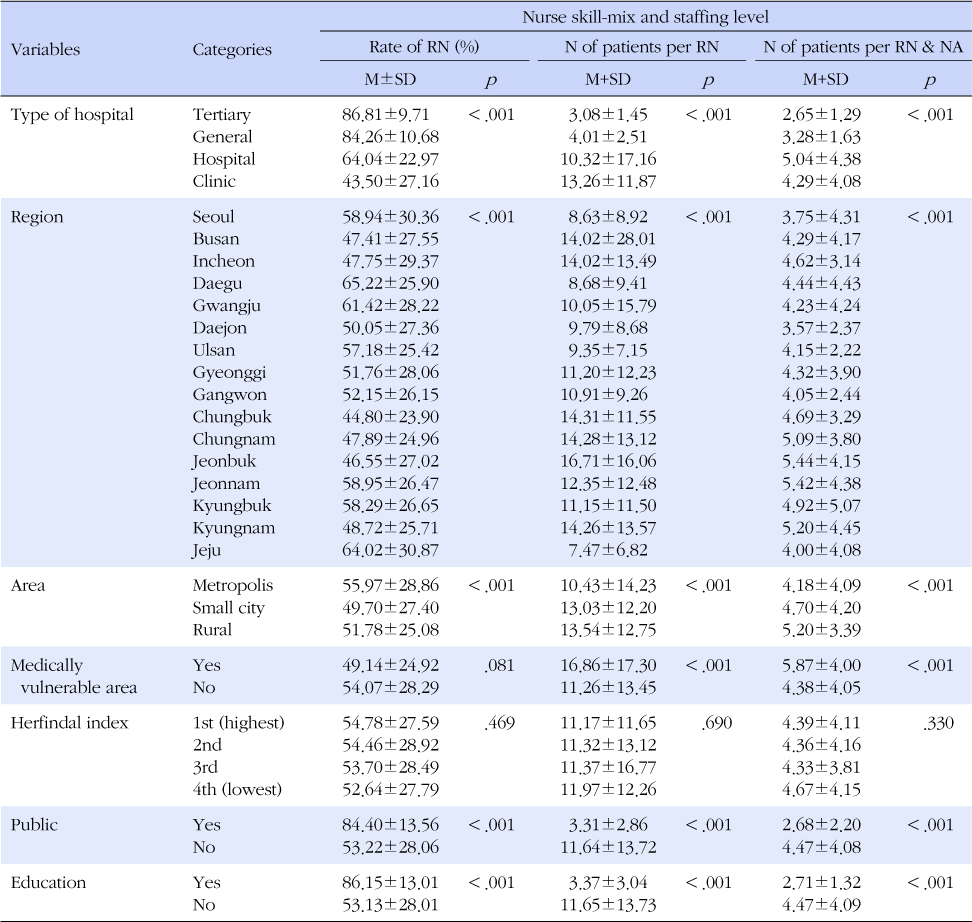
Distribution of Hospitals and Nurse Skill Mix and Staffing Level according to Hospital Characteristics
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant.
Relationship between Nurse Skill Mix and Staffing Level and Hospital Characteristics
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
Hospital Factors affecting to Nurse Skill Mix
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
Hospital Factors affecting Nurse Staffing Level
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic.
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant.
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic resonance imaging.
RN=Registered nurse; NA=Nurse assistant; CT=Computerized tomography; MRI=Magnetic.

