1Ajou Medical Center, Korea.
Copyright © 2013 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
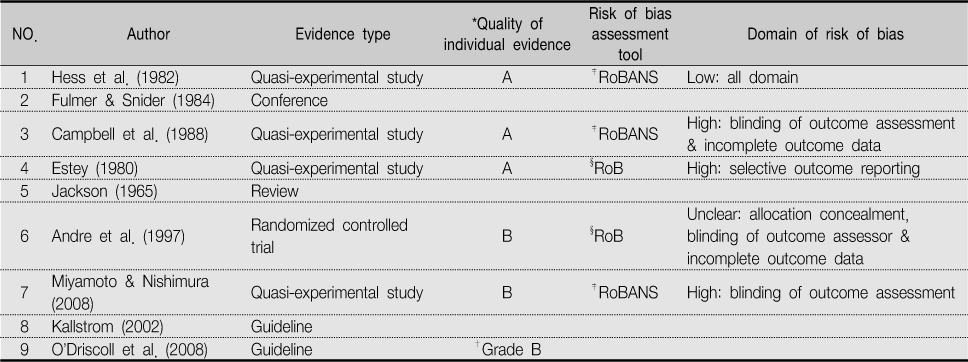
*Quality of individual evidence (used GRADE profiler) A. high: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect; B. moderate: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate; C. low: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate; D. very low: any estimate of fact is very uncertain; †Grading of recommendation (O'Driscoll et al., 2008); ‡RoBANS: Risk of Bias Assessment tool for Non-randomized Study; §RoB: revised Cochrane Risk of Bias.
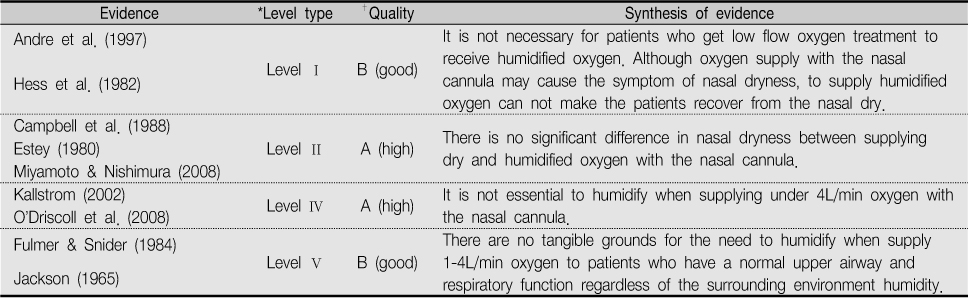
*Level type
Level I: experimental study, randomized controlled trial (RCT), systemic review of RCTs with or without meta-analysis; Level II: quasi-experimental studies, systematic review of a combination RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, or quasi-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis; Level III: non-experimental study, systematic review of a combination of RCTs, quasi-experimental, and non-experimental studies, or non-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis, qualitative study of systematic review of qualitative studies with or without meta-synthesis; Level IV: opinion of respected authorities and/or reports of nationally recognised expert committees/consensus panels based on scientific evidence; Level V: evidence obtained from literature reviews, quality improvement, program evaluation, financial evaluation, or case reports, opinion of nationally recognized expert(s) based on experimental evidence
†Dearholt & Dang (2012). p233, Appendix C: Evidence level and quality guide.

Appraisal of Individual Evidence and Assessment Risk of Bias
*Quality of individual evidence (used GRADE profiler) A. high: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect; B. moderate: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate; C. low: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate; D. very low: any estimate of fact is very uncertain; †Grading of recommendation (O'Driscoll et al., 2008); ‡RoBANS: Risk of Bias Assessment tool for Non-randomized Study; §RoB: revised Cochrane Risk of Bias.
Evidence Level, Quality Guide and Evidence Synthesis of JHNEBP
*Level type
Level I: experimental study, randomized controlled trial (RCT), systemic review of RCTs with or without meta-analysis; Level II: quasi-experimental studies, systematic review of a combination RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, or quasi-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis; Level III: non-experimental study, systematic review of a combination of RCTs, quasi-experimental, and non-experimental studies, or non-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis, qualitative study of systematic review of qualitative studies with or without meta-synthesis; Level IV: opinion of respected authorities and/or reports of nationally recognised expert committees/consensus panels based on scientific evidence; Level V: evidence obtained from literature reviews, quality improvement, program evaluation, financial evaluation, or case reports, opinion of nationally recognized expert(s) based on experimental evidence
†Dearholt & Dang (2012). p233, Appendix C: Evidence level and quality guide.
Levels of Evidence and Grade of Recommendations by the *EORTC
*EORTC=European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer
*Quality of individual evidence (used GRADE profiler) A. high: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect; B. moderate: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate; C. low: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate; D. very low: any estimate of fact is very uncertain; †Grading of recommendation (
*Level type Level I: experimental study, randomized controlled trial (RCT), systemic review of RCTs with or without meta-analysis; Level II: quasi-experimental studies, systematic review of a combination RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, or quasi-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis; Level III: non-experimental study, systematic review of a combination of RCTs, quasi-experimental, and non-experimental studies, or non-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis, qualitative study of systematic review of qualitative studies with or without meta-synthesis; Level IV: opinion of respected authorities and/or reports of nationally recognised expert committees/consensus panels based on scientific evidence; Level V: evidence obtained from literature reviews, quality improvement, program evaluation, financial evaluation, or case reports, opinion of nationally recognized expert(s) based on experimental evidence †Dearholt & Dang (
*EORTC=European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer