1Professor, Department of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Korea.
2Doctoral Student, Department of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Korea.
Copyright © 2010 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration

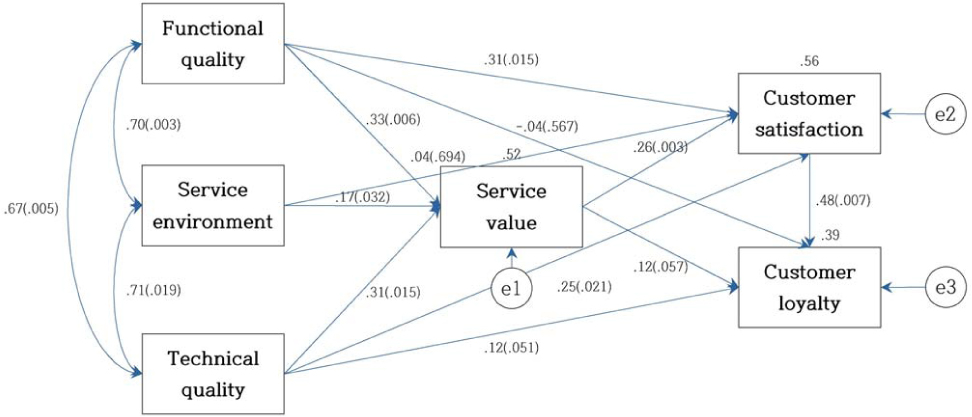
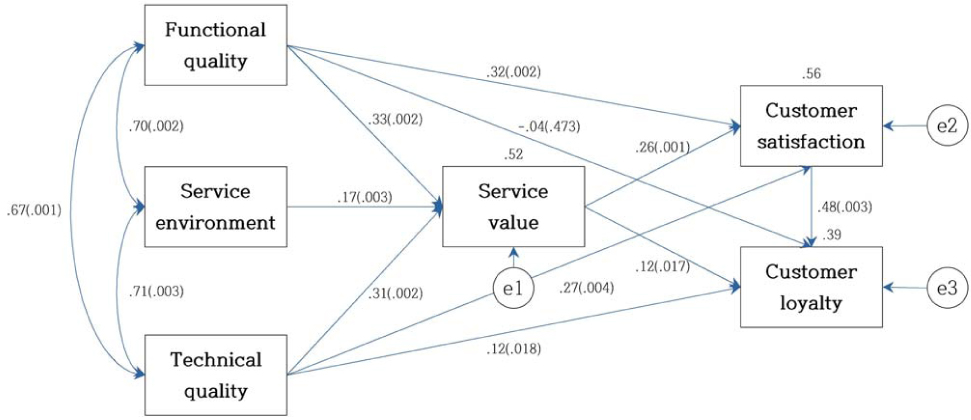
Demographic characteristics (N=654)
Means, standard deviations and correlations of variables
Goodness fit indies for the hypothetical and modified models
GFI=goodness of fit index; AGFI=ajusted goodness of fit index; RMR=root mean squared residual, RMSEA=root mean squared error of approximation; NFI=normed fit index; CFI=comparative fit index); TLI=tucker-lewis index.
Standardized direct effect, indirect effect and total effect in modified path model
SMC=Squared multiple correlations.
GFI=goodness of fit index; AGFI=ajusted goodness of fit index; RMR=root mean squared residual, RMSEA=root mean squared error of approximation; NFI=normed fit index; CFI=comparative fit index); TLI=tucker-lewis index.
SMC=Squared multiple correlations.

