1Director, Department of Nursing, Seoul National Hospital, Korea.
2Full-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Korea.
3Researcher, Jeju regional Cancer Center, Korea.
4Head nurse, Department of Nursing, Seoul National Hospital, Korea.
5Former QA team nurse, Department of Nursing, Seoul National Hospital, Korea.
Copyright © 2010 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration

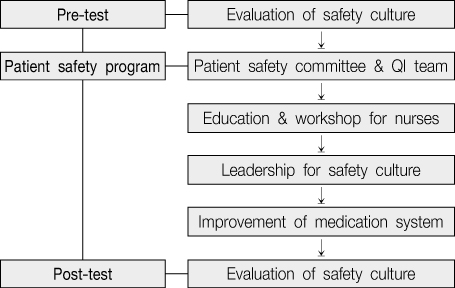
Patient safety program activities
Homogeneity test of general characteristics between before and after groups
Mean differences of safety culture in criteria
*the reverse value
Mean differences of safety culture between nurses' and nurse managers'
*the reverse value
Mean differences in the safety culture by career and unit
*the reverse value
*the reverse value