1Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Korea.
2Full-time lecturer, Department of Nursing, Woosong University, Korea.
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration

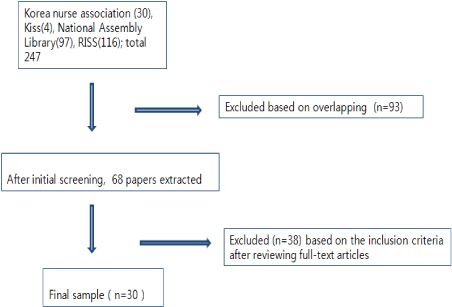
List of Reviewed Articles (n=30)
Types and Location of Hospitals in Articles by Year
Distribution of Number of Nurse Subjects and Hospitals (n=30)
Tools and Mean of Turnover Intention (n=30)
Related General Characteristics to Turnover Intention (n=30)
T.I. ; Turnover Intention
Related Variables to Turnover Intention by Correlation Analysis (n=30)
Affected Variables to Turnover Intention by Regression Analysis (n=30)
T.I. ; Turnover Intention