1Professor, Department of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Korea.
2Professor, Department of Nursing, Kwandong University, Korea.
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration

Demographic Characteristics (N=393)
Means and Correlations among Variables
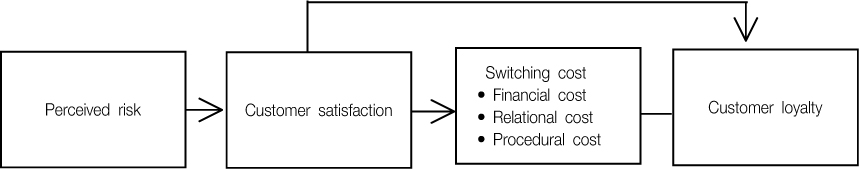
Standardized Direct Effect, Indirect Effect, and Total Effect in the Modified Model
SMC =squared multiple correlations.
SMC =squared multiple correlations.