1Professor, College of Nursing, Chonnam National University; Research Institute of Nursing Science, Chonnam National University, Korea.
2RN, PhD, Kidney Center, Department of Nursing, Chonnam National University Hospital, Korea.
3Full-time Instructor, Department of Nursing, Jeonbuk Science College; Research Institute of Nursing Science, Chonnam National University, Korea.
Copyright © 2011 Korean Academy of Nursing Administration
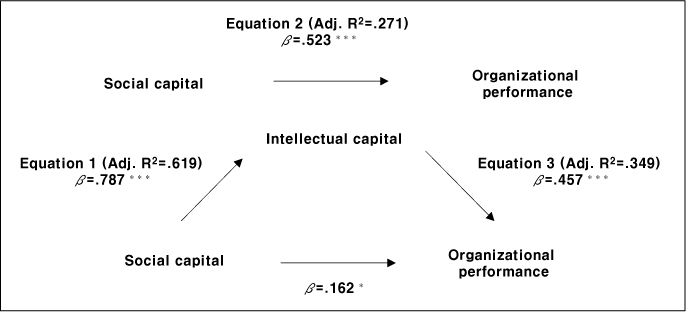
***p<.001, *p<.05
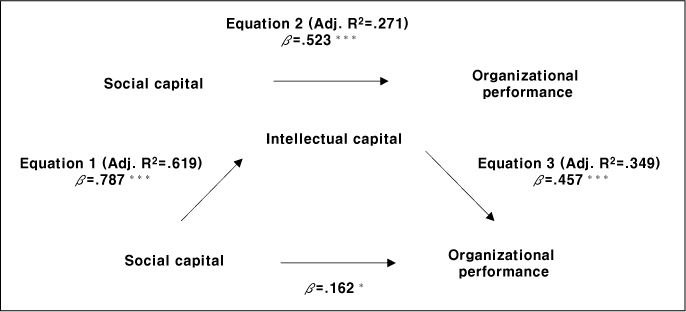
SC=Social capital; IC= Intellectual capital; OP=Organizational performance
Equation 1. IV → mediator to check beta and R2; Equation 2. IV DV to check beta and R2
(it should be significant to test mediator effect);
Equation 3. Step 1: mediator DV to check beta and R2; Step 2: IV DV to check beta and R2.
Z-value=a×b/SQRT(b2×Sa2+a2×Sb2); a=raw (unstandardized) regression coefficient for the association between IV and mediator;
Sa=standard error of a; b=raw coefficient for the association between the mediator and the DV (when the IV is also a predictor of the DV); Sb=standard error of b.

Validity and internal reliability of social capital, intellectual capital scale
General characteristics (N=390)
*Specialty nursing unit= ICU (intensive care unit), ER (emergency room), DR (delivery room), OR (operation room), AK (artificial kidney), OPD (out patient department).
Descriptive statistics of study variables (N=390)
Correlation of variables (N=390)
***p<.001
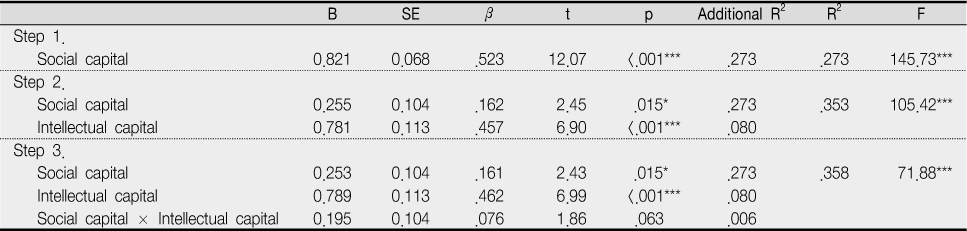
Moderating effects of intellectual capital in the relationship between social capital and organizational performance (N=390)
***p<.001, *p<.05
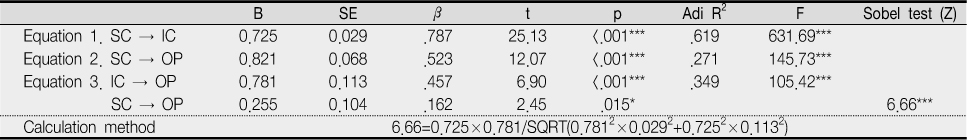
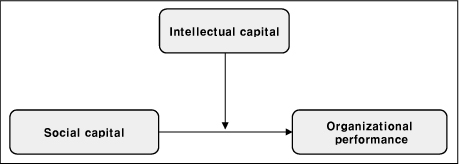
Mediating effects of intellectual capital in the relationship between social capital and organizational performance (N=390)
***p<.001, *p<.05
SC=Social capital; IC= Intellectual capital; OP=Organizational performance
Equation 1. IV → mediator to check beta and R2; Equation 2. IV DV to check beta and R2
(it should be significant to test mediator effect);
Equation 3. Step 1: mediator DV to check beta and R2; Step 2: IV DV to check beta and R2.
Z-value=a×b/SQRT(b2×Sa2+a2×Sb2); a=raw (unstandardized) regression coefficient for the association between IV and mediator;
Sa=standard error of a; b=raw coefficient for the association between the mediator and the DV (when the IV is also a predictor of the DV); Sb=standard error of b.
*Specialty nursing unit= ICU (intensive care unit), ER (emergency room), DR (delivery room), OR (operation room), AK (artificial kidney), OPD (out patient department).
***p<.001
***p<.001, *p<.05
***p<.001, *p<.05 SC=Social capital; IC= Intellectual capital; OP=Organizational performance Equation 1. IV → mediator to check beta and R2; Equation 2. IV DV to check beta and R2 (it should be significant to test mediator effect); Equation 3. Step 1: mediator DV to check beta and R2; Step 2: IV DV to check beta and R2. Z-value=a×b/SQRT(b2×Sa2+a2×Sb2); a=raw (unstandardized) regression coefficient for the association between IV and mediator; Sa=standard error of a; b=raw coefficient for the association between the mediator and the DV (when the IV is also a predictor of the DV); Sb=standard error of b.