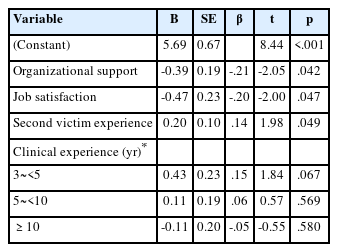
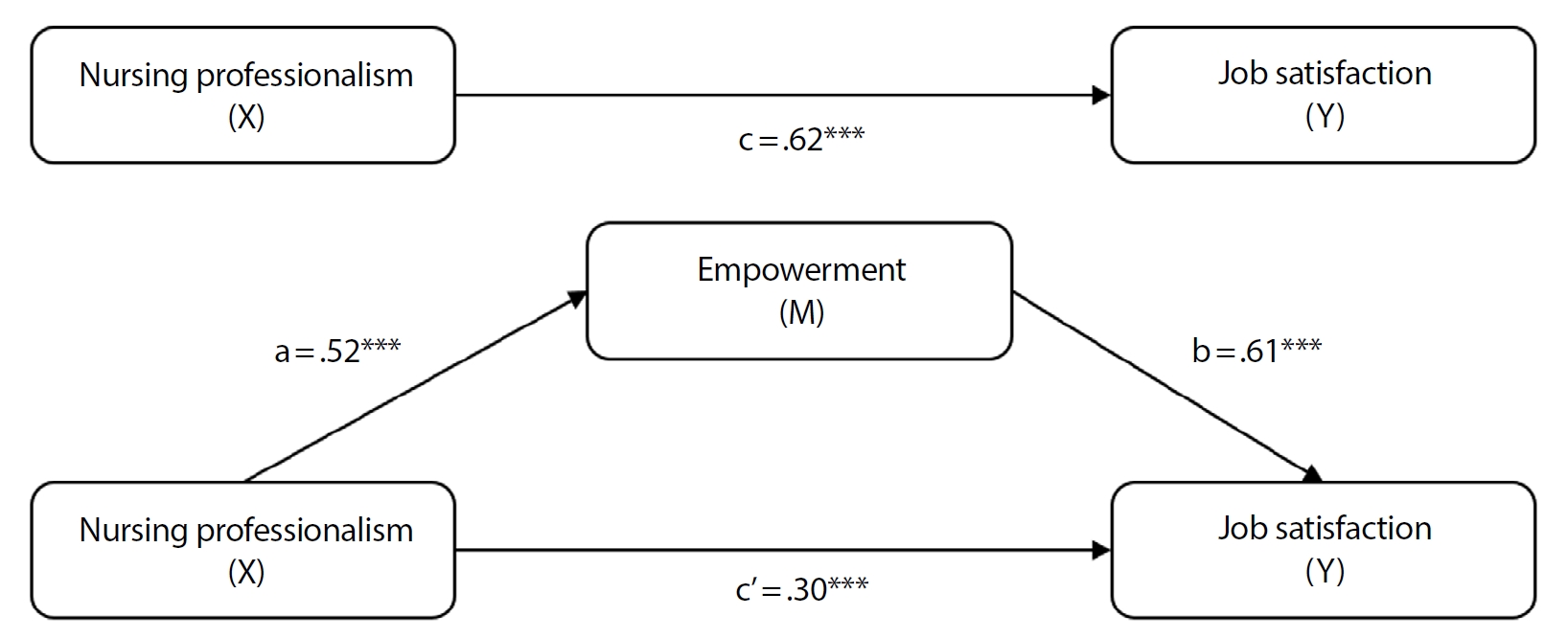
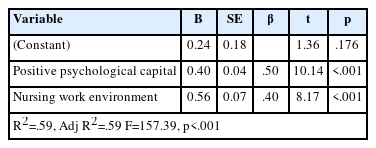
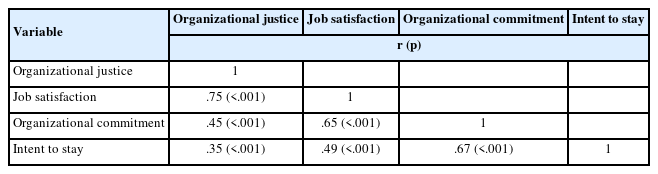
Citations

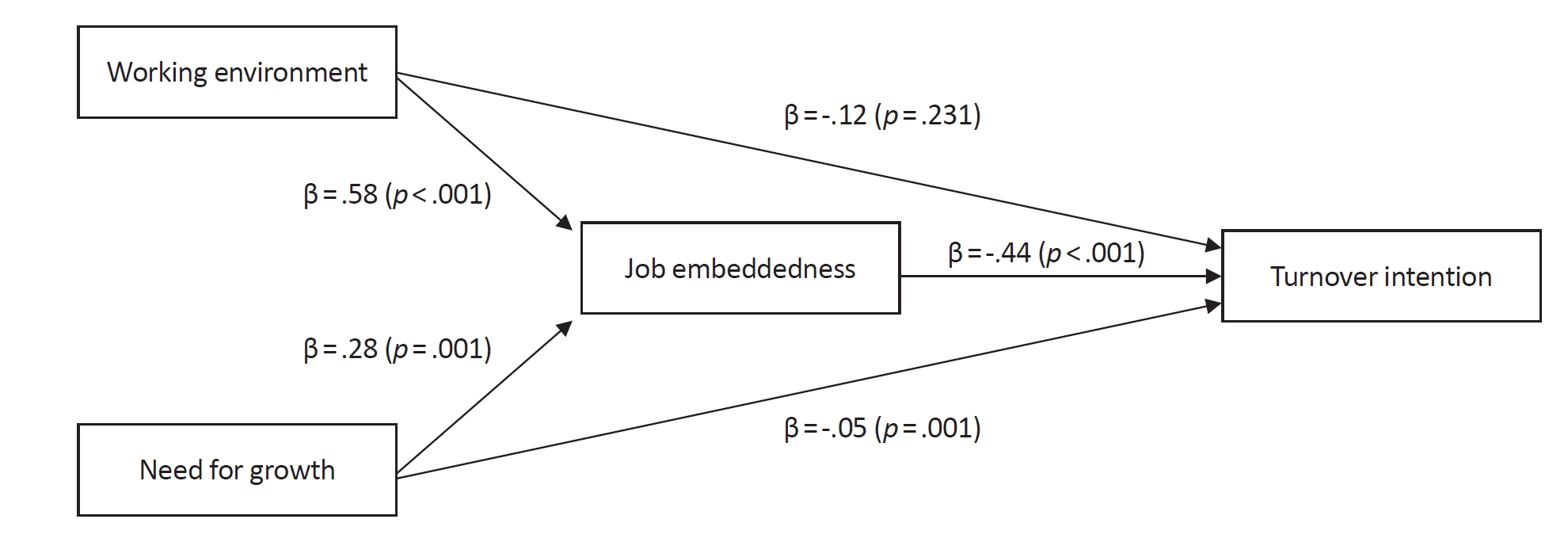
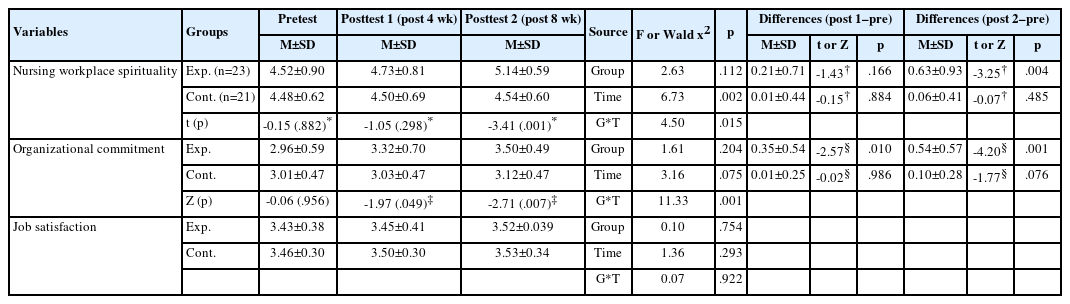
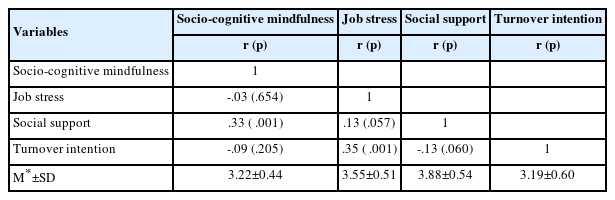
Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations

Citations


